Fields
Field nodes are essentially 3D gradients that can be used to control the output value of many different data/node types in Octane (figure 1).
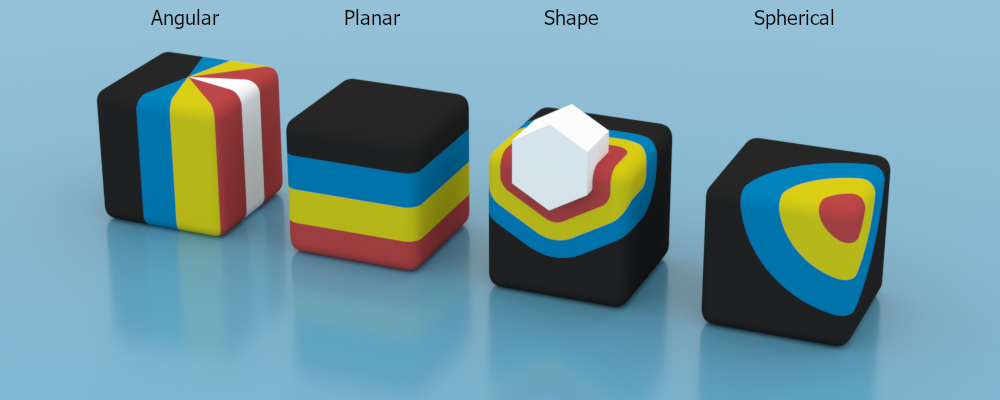
Figure 1: The four field types used in conjunction with a 4-color gradient
The four field types available are:
Angular
Planar
Shape
Spherical
Angular
Similar to the angular gradient but has additional options to map the angle to the gradient value.

angular field
Falloff Angles X & Y
Angular distance at which the value falls down to zero, for each side of the core sector.
Core Angle
Angular range of the core sector in which the value is one.
Planar
Similar to the linear gradient but with a finite mapping.
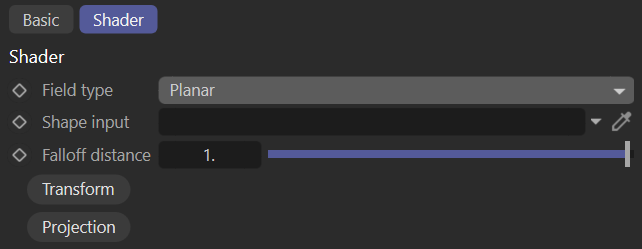
planar field
Falloff Distance
Distance from the plane at which the value falls down to zero.
Shape
Maps the distance between Vectron/SDF objects.
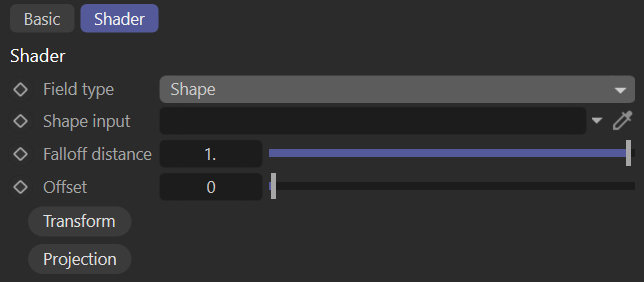
shape field
Shape Input
Signed distance field representing the shape inside which the value is one.
Falloff Distance
Distance at which the value falls down to zero.
Offset
Offset applied to the core shape surface at which the value starts falling off from one.
Spherical
Maps the distance of the origin in UVW space to a (clamped) gradient value.
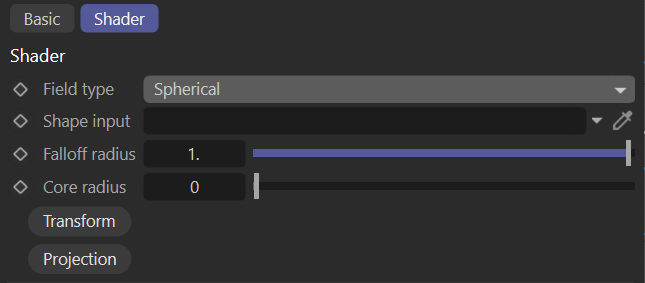
spherical field
Falloff Radius
Radius at which the value falls down to zero.
Core Radius
Radius of the spherical core in which the value is one.
